Irritation in the Patellar Tendon: Causes Damage to Tendon
What causes irritation and damage to the patellar tendon?
The patella also called the kneecap, is the convex bone that sits in front of the knee joint. The patellar tendon connects the patella bone to the tibia. It facilitates movement and allows us to perform daily movements like walking, jumping and running.
Repeated excessive stress on the patellar tendon through rigorous physical activities can cause the tendon to become inflamed. The resulting irritation and pressure on the tendon can lead to long term pain and discomfort.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Patellar Tendonitis
Patellar tendon pain syndrome is a direct result of excessive stress on the knee joint. This sensation is fairly common in athletes and people in jobs with long sitting hours. A physical examination helps doctors assess the severity of the trauma.
-
Imaging Tests
External swelling or redness of the knee joint are rarely visible. Instead, doctors rely on sophisticated technology like Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and X-Ray imaging to diagnose the condition.
-
Doctor and Physiotherapist
In most cases, one side of the tendon is affected but in 20-30% of cases, both sides may be affected and may require additional care. Practitioners often compare both knees of a patient to gain a better understanding of the extent of the condition
-
Symptoms
In mild cases, a patient usually experiences pain in the lower leg under any stress. A patient might also experience a “pulling” or “tightening” sensation in the knee joint.
Immediate medical treatment is highly recommended to manage the long term risks of degeneration and chronic pain. Excessive wear and tear of the kneecap can lead to a loss in strength of the thigh muscle and further restrict one’s mobility.
Treatment from Irritation in the Patellar Tendon
Treatment for kneecap pain is mostly conservative i.e. non-surgical. Full recovery from the condition is possible following a complete treatment plan with sufficient rest and the use of medical knee support.
Non-Surgical Treatment for Patellar Irritation
-
Reduce Painful Activity
Relaxation and relief from all external stress is the first step in all cases of patellar tendon pain syndrome. The tendon should be left to rest, and a knee brace should be used to provide ample support and restrict movement and pressure on the knee joint.
*Note- Ample recovery time is recommended, even if the pain symptoms subside, to ensure complete healing. Any stressful activities like bending the knee, walking, sports should be immediately suspended.
-
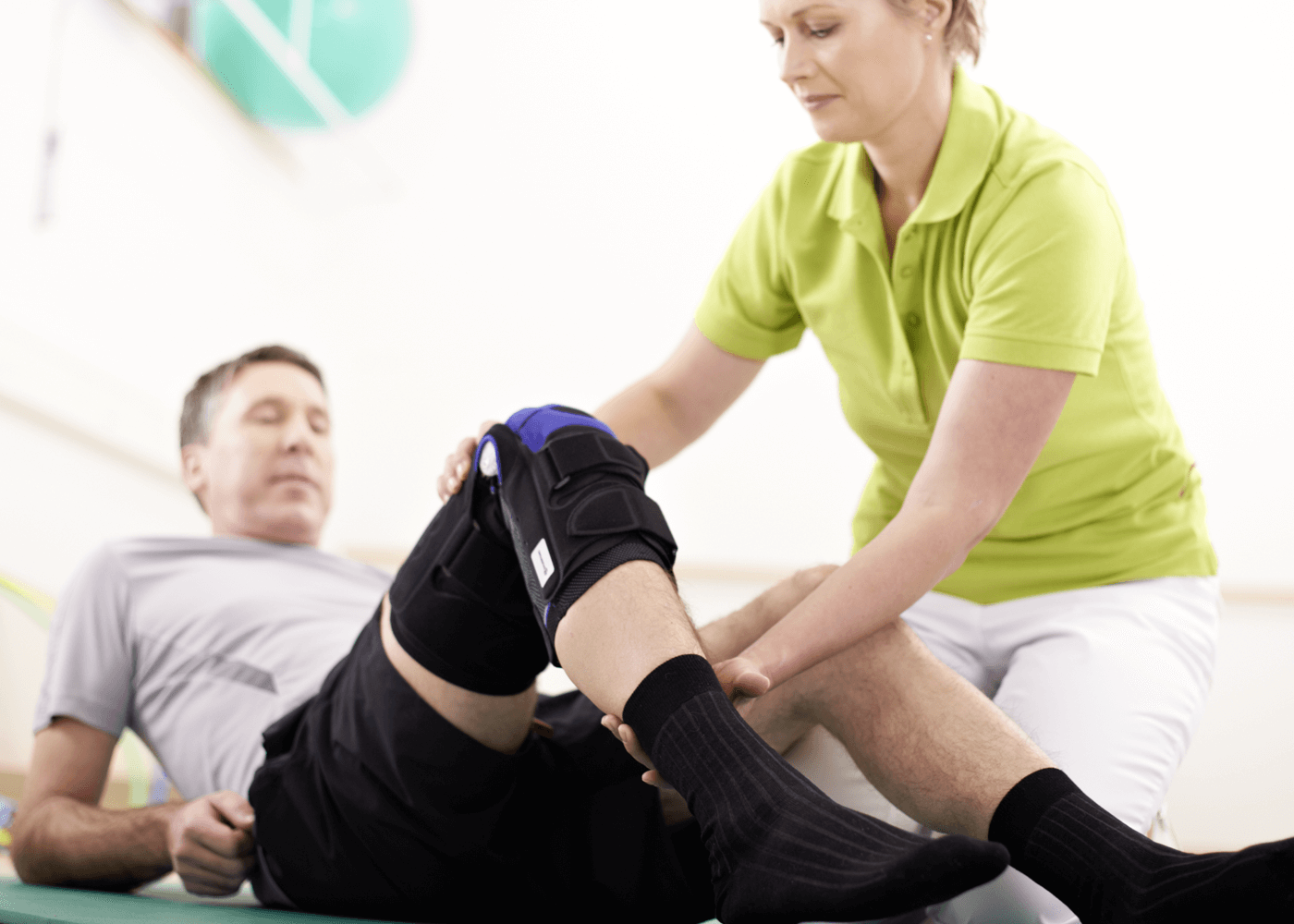
Rehabilitation And Physiotherapy
The patellar tendon is strong and resilient. Prescribed rehabilitation, like hydrotherapy and remedial massage, can help boost blood circulation and facilitate healing.
Regulated physiotherapy is a proven effective treatment path. The exercises can help promote the reorganization of the tendon and facilitate recovery.
Encouraging healthy proprioception and strengthening of the tendon aids to prevent long term degeneration of the knee joint and further injury.
-
Prescribed Painkillers
Such as Ibuprofen or Panadol can be used to help alleviate pain and discomfort in patients. Pain, however, is a crucial indicator of the injury.
Painkillers merely mask the pain without addressing the underlying condition. Long term use of painkillers has side-effects and can be counter-productive.
-
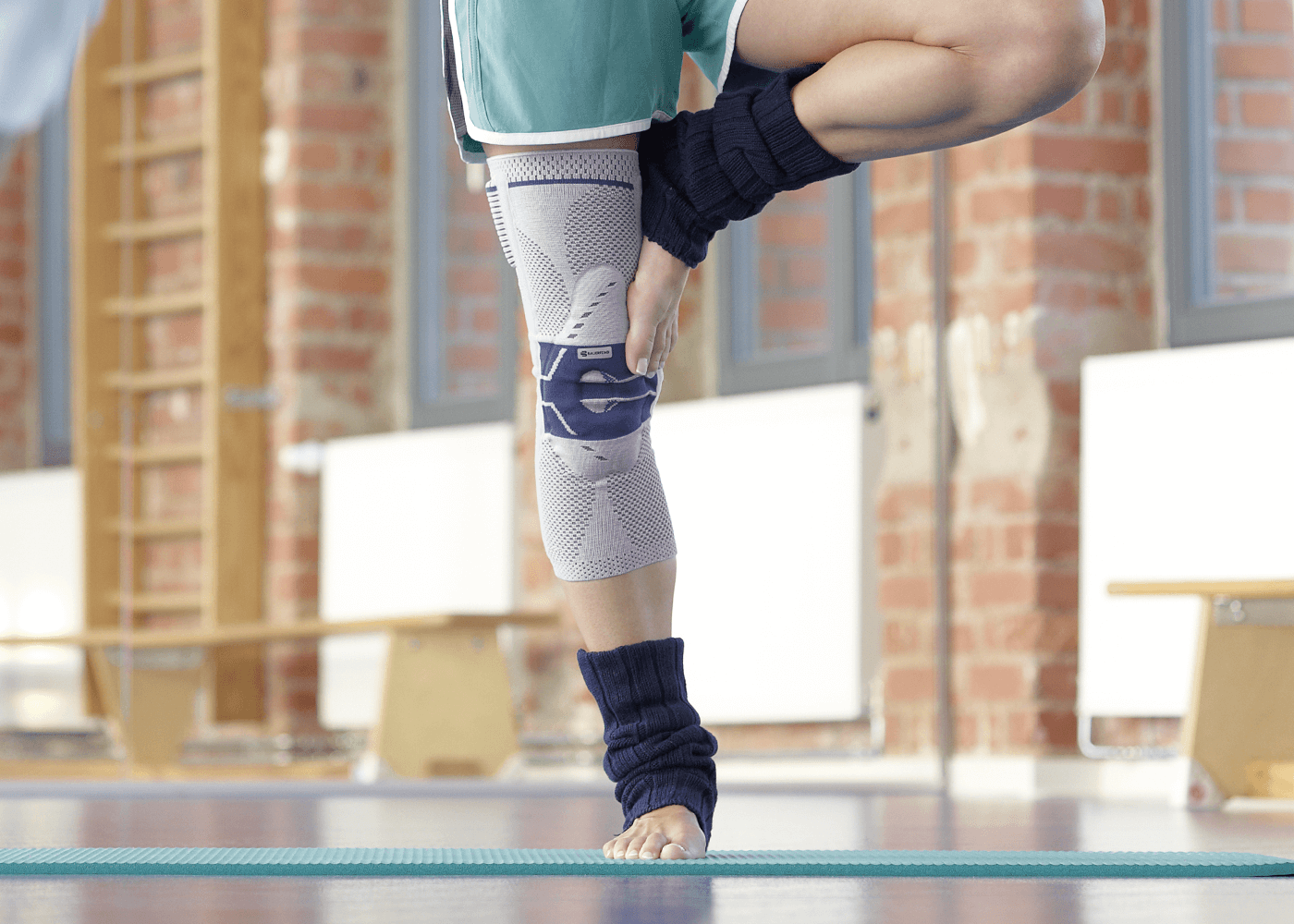
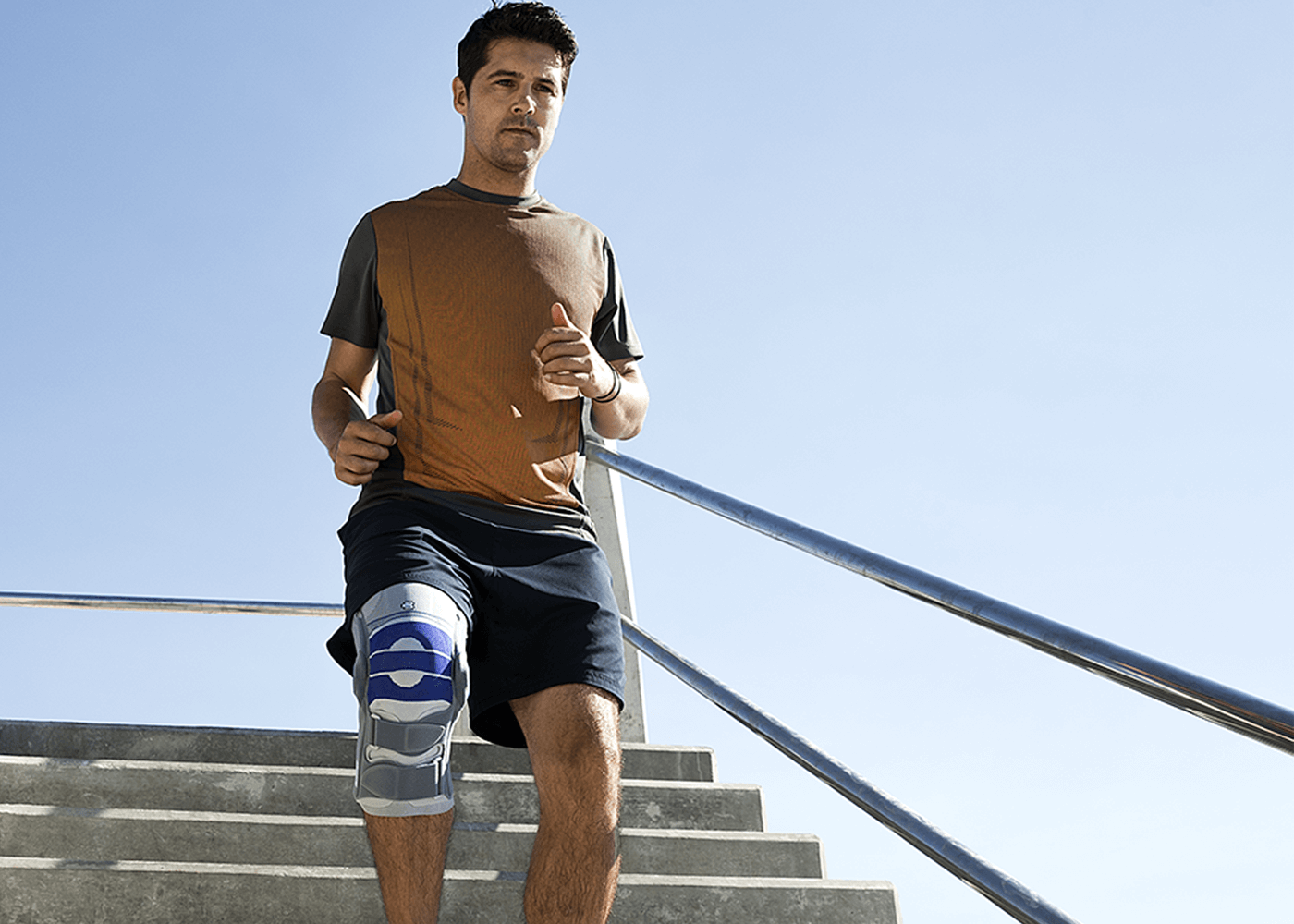
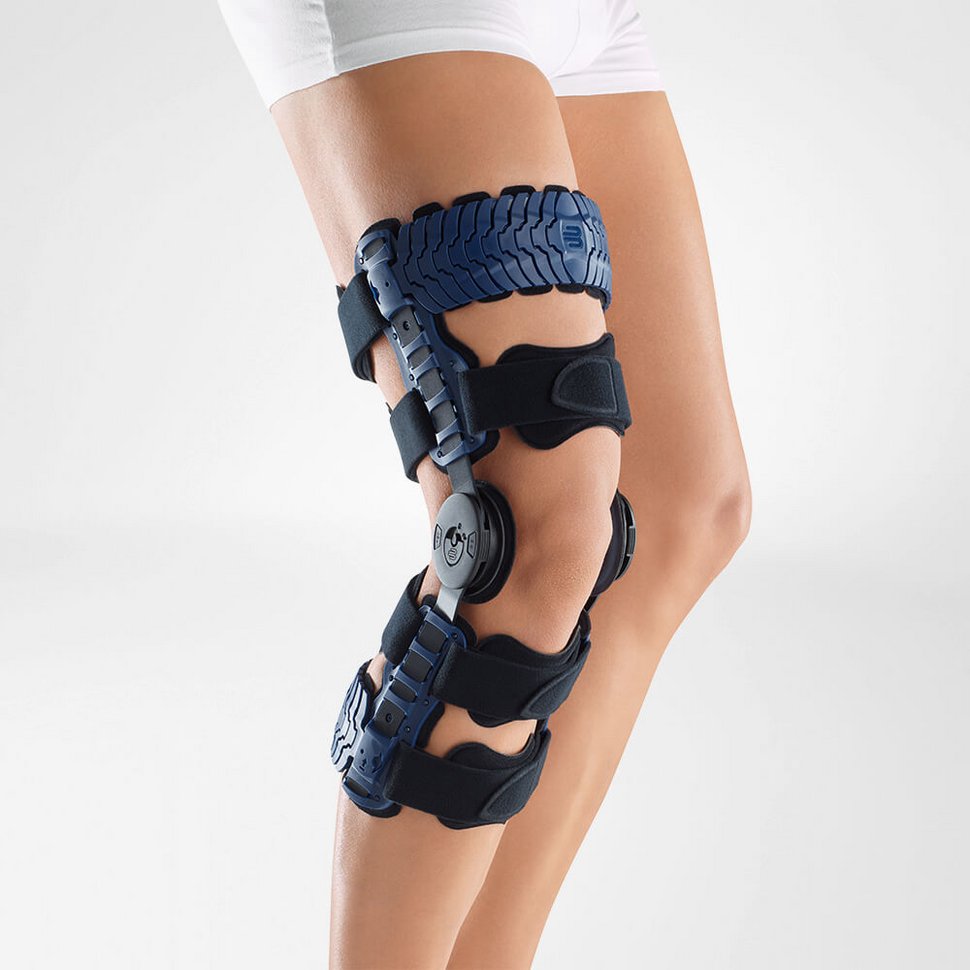
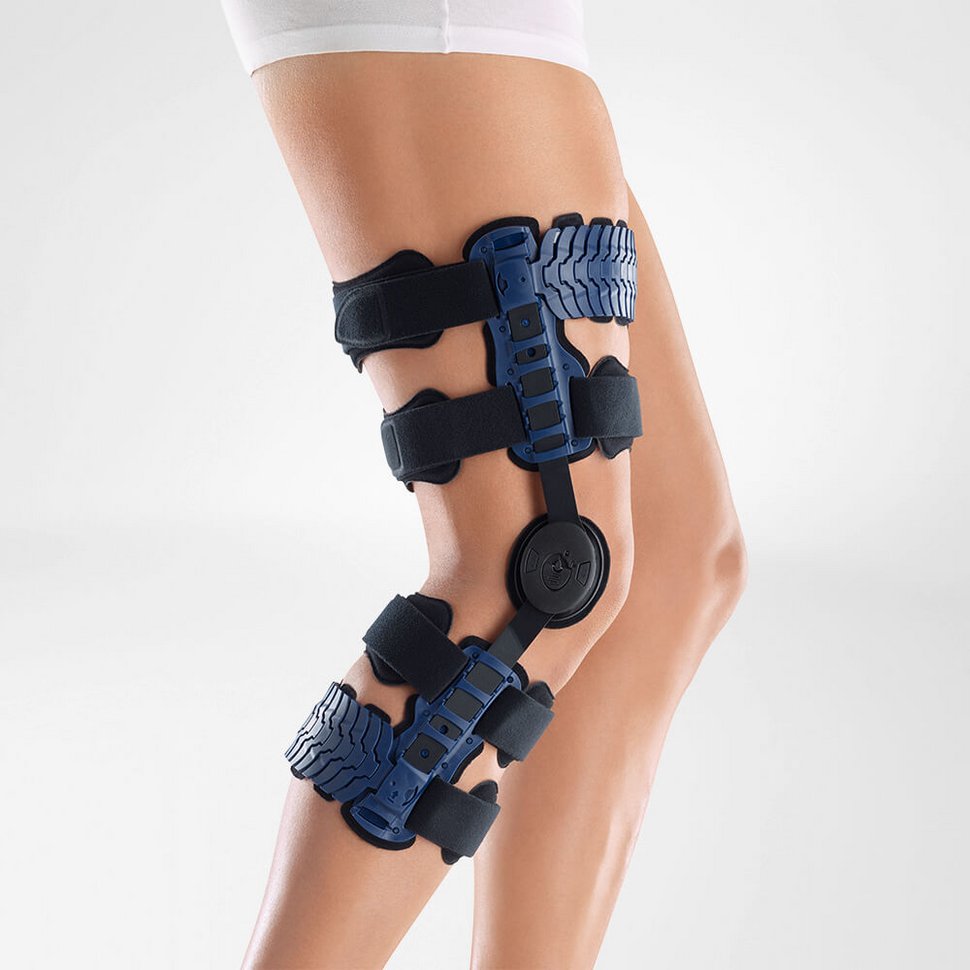
Medical Knee Braces
Complete healing and recovery are crucial, and it is highly recommended to provide ample support to the tendon through the use of a medical knee brace.
Knee braces provide:
- targeted compression to help boost circulation and
- reduce the possibility of effusions and edema.
Wearing a Bauerfeind knee brace, like the GenuPoint or GenuTrain, can minimize your chances of injury by providing enhanced stability, proprioception and medical-grade compression. The support found in Bauerfeind’s braces is unmatched and can be instrumental in a speedy recovery.
Surgical Intervention
Operative surgery is considered when all conservative treatments have been exhausted, where symptoms are persistent and severe.
Arthroscopy can be conducted, where inflamed areas of the patellar tendon and surrounding tissue are removed. Surgery is risky and should be opted only as a last resort.
Stabilization through Orthoses to prevent patellar damage
Prevention of the condition covers a range of options. Awareness of the limitations of the knee joint and good proprioception goes a long way in managing the stress imposed on the knee. Medical knee braces are a valuable tool to both prevent and manage patellar tendon pain syndrome.
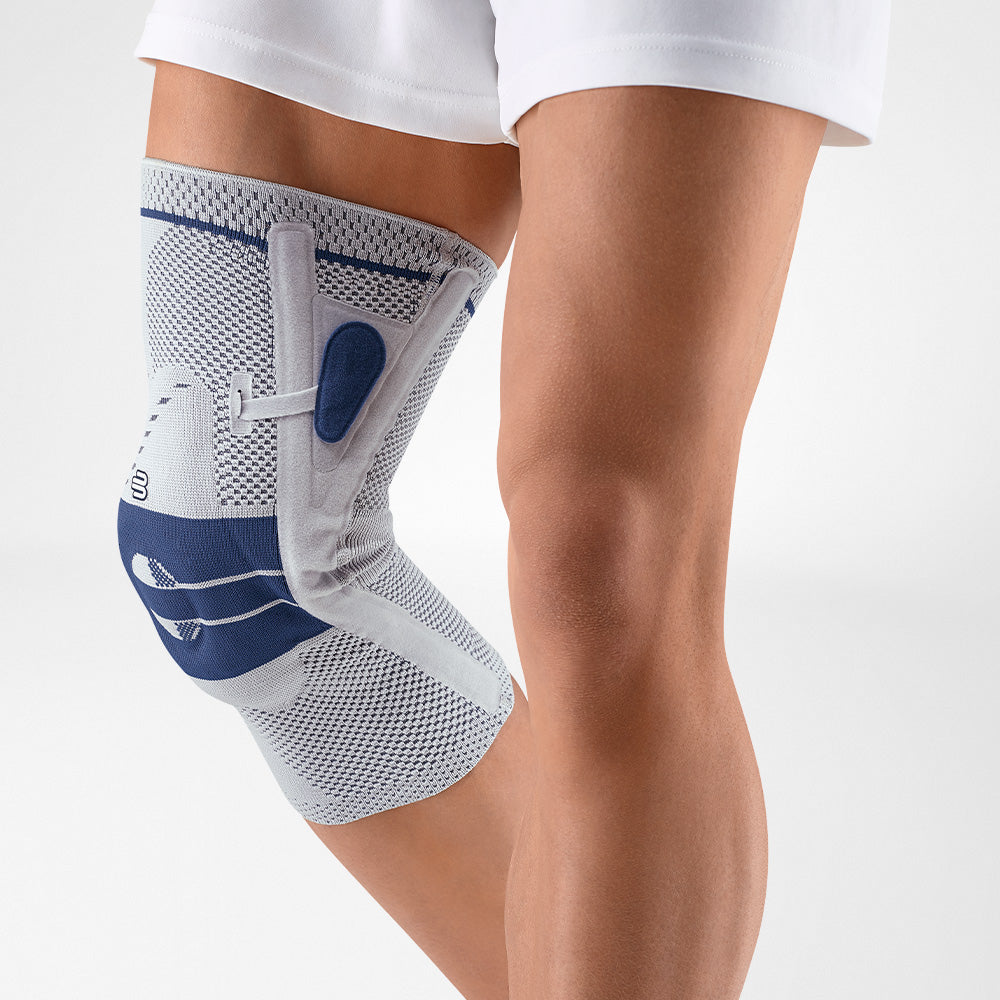
How does a patellar tendon strap treat patellar tendon irritation?
Bauerfeind offers premium German-engineered knee braces that are well researched and manufactured with materials (non-neoprene based) to the highest standards to provide the very best in comfort and support.
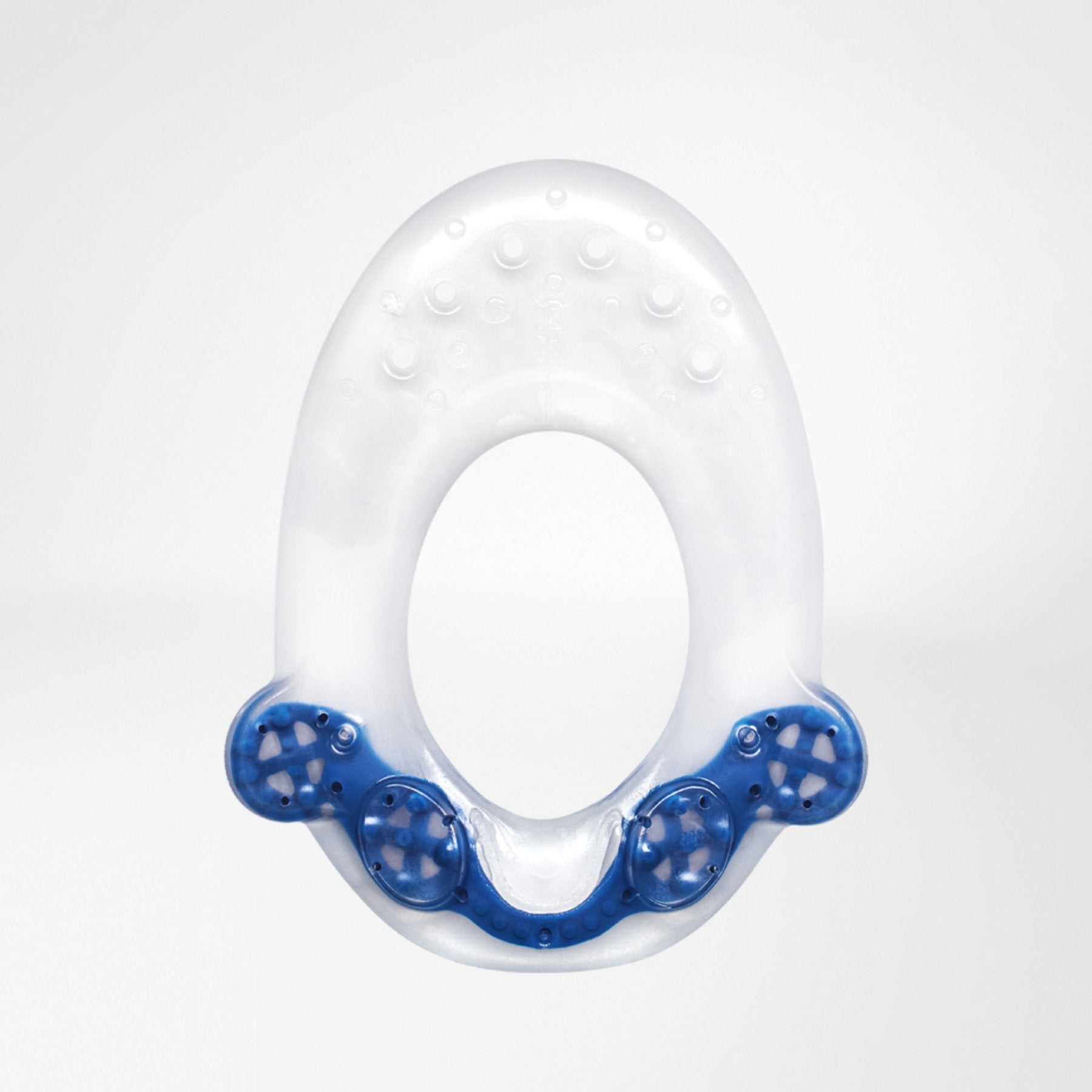
The GenuPoint knee strap is anatomically shaped and fits perfectly around the knee. It features a thin massaging gel pad, consisting of 4 pressure points, which help soothe the patella tendon and relieve pain during movement.


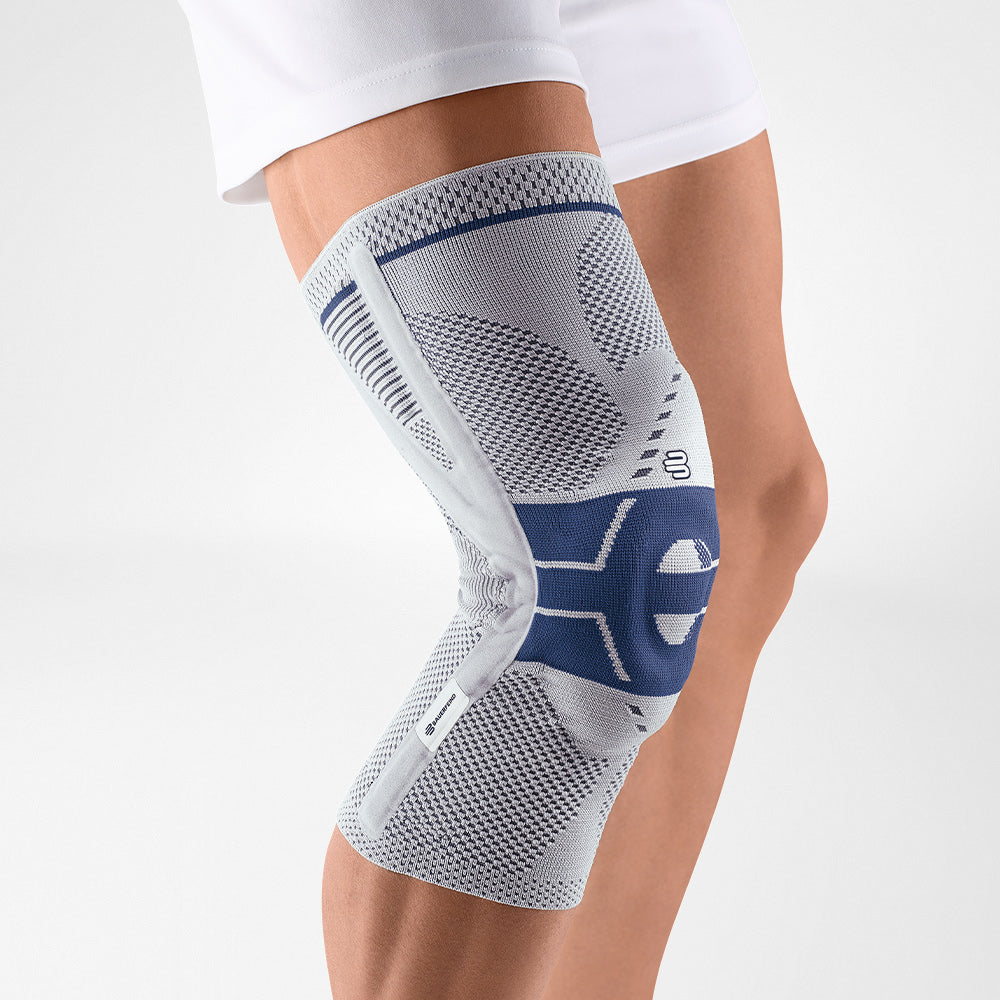
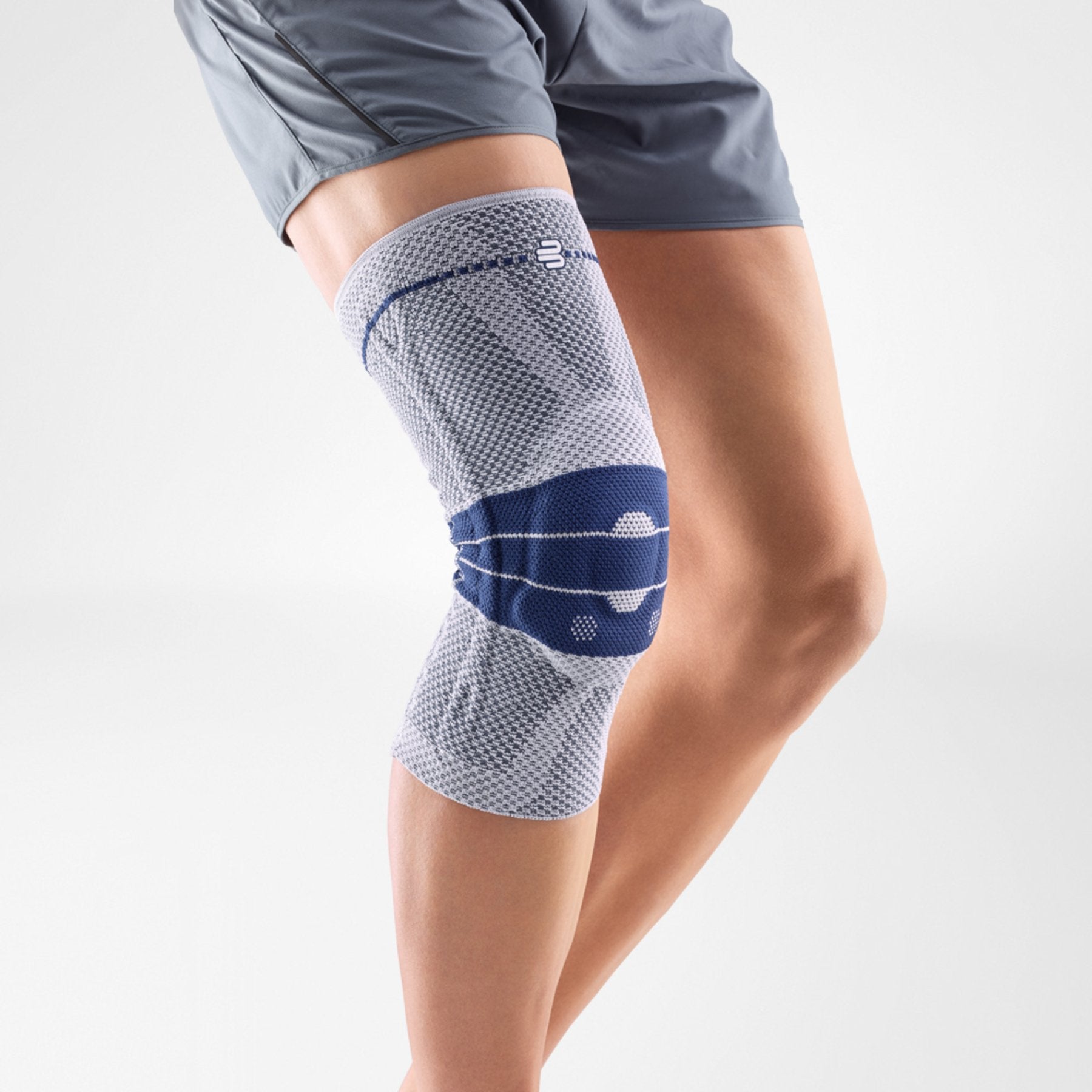
How does a medical knee brace treat patellar tendon pain?
The GenuTrain knee brace is a very suitable knee brace to be worn to recover from and protect against developing patella tendon pain syndrome.This brace features an Omega+ gel pad, with integrated massage points, which help to:
- relieve pain and
- reduce inflammation in the tendon.
Medical grade compression is also engineered into the GenuTrain knee brace’s lightweight knit fabric to promote blood circulation within the knee joint.